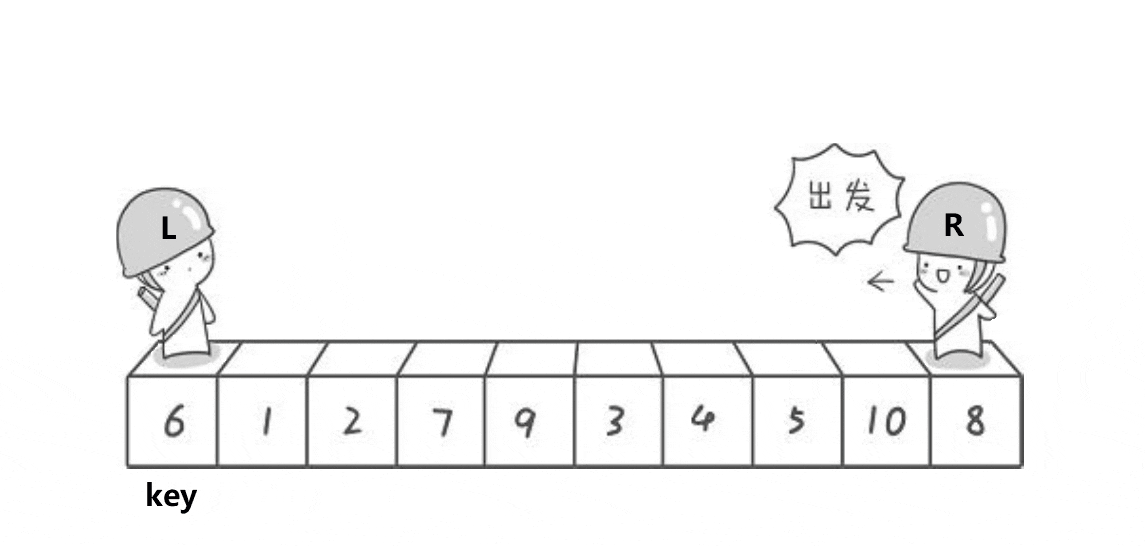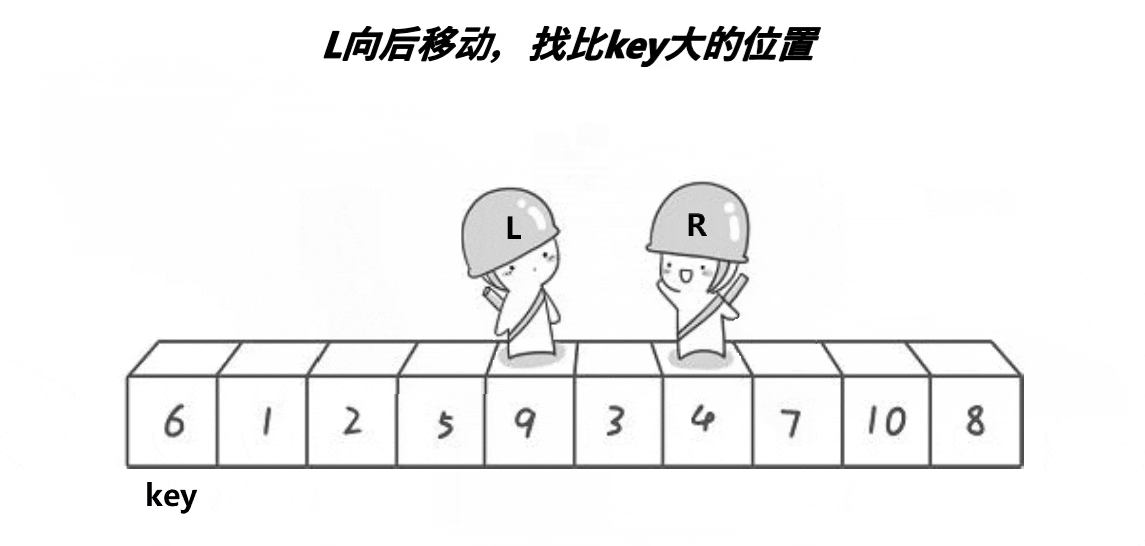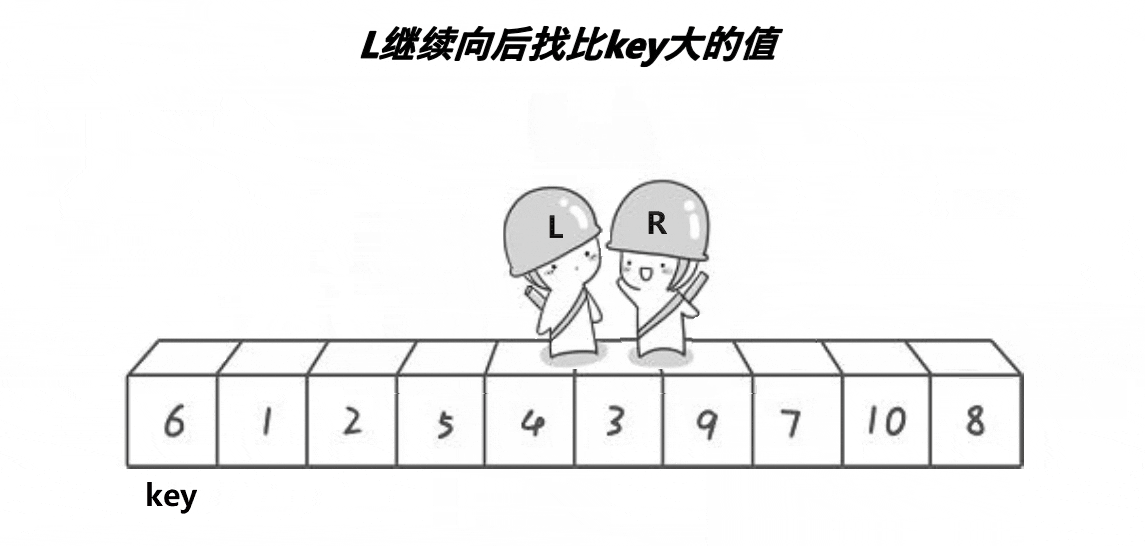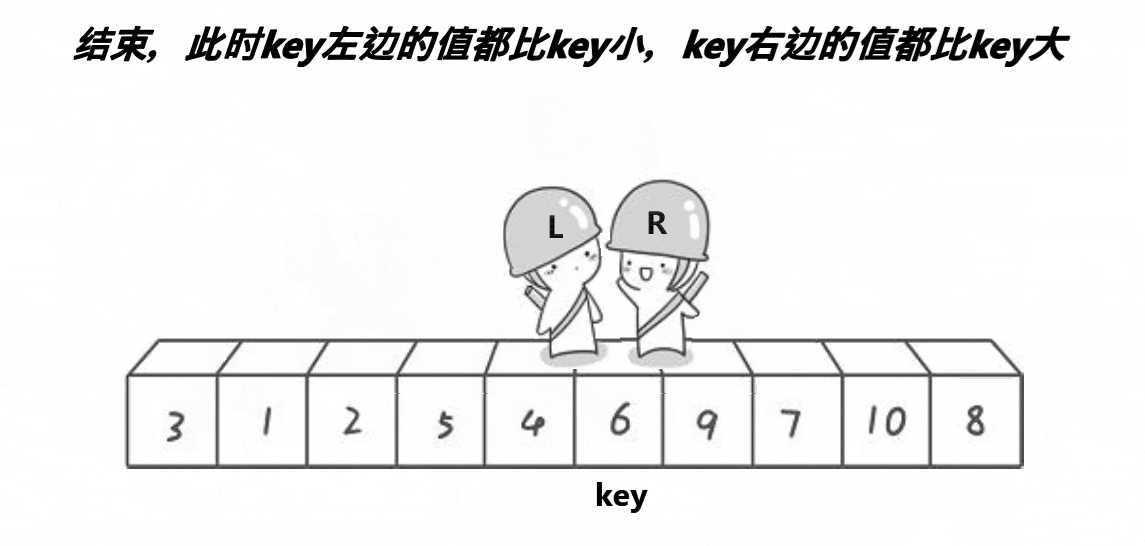
🧑🏻💻 排序
记录了 C++ 中几种排序方法的实现。作笔记用。
Characteristics of sorting algorithms:
In-place: a sorting algorithm is in-place if $O(1)$ extra space is needed beyond input.
Stability: a sorting algorithm is stable if numbers with the same value appear in the output array in the same order as they do in the input array.
Procedure 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐞𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭1
In: An array $A$ of $n$ integers.
Out: A permutation of that array $A$ that is sorted (monotonic).
for $i := 2$ to $A.length$
$key := A[i]$
// Insert $A[i]$ into the sorted subarray $A[1 : i - 1]$
$j := i - 1$
while $j > 0$ and $A[j] > key$
$A[j + 1] := A[j]$
$j := j - 1$
$A[j + 1] := key$
return $A$
One possible implementation with C++:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
int main()
{
int arr[100], len;
cin >> len;
for (int t = 0; t < len; t++)
cin >> arr[t];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
int key = arr[i]; // 把要比较的牌从手牌里单独抽出来
int j = i - 1;
while (j > 0 && arr[j] > key) // 将此牌与前面的牌比较大小
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; // 把前面的大牌依次往后挪,空出位置
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key; // 把此牌插入合适的位置
}
for (int t = 0; t < len; t++)
cout << arr[t] << " ";
return 0;
}
Procedure 𝐌𝐞𝐫𝐠𝐞-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
In: An array $A$ of $n$ integers.
Out: A permutation of that array $A$ that is sorted (monotonic).
MergeSort($A[1…n]$):
if $n = 1$
$sol[1…n] = [1…n]$
else
$solLeft[1…(n/2)] := MergeSort(A[1…(n/2)])$
$solRight[1…(n/2)] := MergeSort(A[(n/2 + 1)…n])$
$sol[1…n] := Merge(solLeft[1…(n/2)], solRight[1…(n/2)])$
return $sol[1…n]$
Merge($A[1…n], B[1…m]$):
$Aindex := 1, Bindex := 1, Result := [ ]$
// Scan $A$ and $B$ from left to right,
// Append the currently smallest to the result array.
while $Aindex \leq A.length$ and $Bindex \leq B.length$
if $A[Aindex] \leq B[Aindex]$
$Result.AddLast(A[Aindex])$
$Aindex := Aindex + 1$
else
$Result.AddLast(B[Bindex])$
$Bindex := Bindex + 1$
// Copy the remaining elements of A and B
while $Aindex \leq A.length$
$Result.AddLast(A[Aindex])$
$Aindex := Aindex + 1$
while $Bindex \leq B.length$
$Result.AddLast(B[Bindex])$
$Bindex := Bindex + 1$
return $Result$
One possible implementation with C++:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
void merge(int a[], int result[], int left, int mid, int right)
{
int i = left, j = mid + 1, k = left;
// 按大小顺序依次添加到 result 数组中
while (i <= mid && j <= right)
{
if (a[i] <= a[j])
result[k++] = a[i++];
else
result[k++] = a[j++];
}
// 处理剩余的数
while (i <= mid)
result[k++] = a[i++];
while (j <= right)
result[k++] = a[j++];
for (i = left; i <= right; i++)
a[i] = result[i];
}
void merge_sort(int a[], int result[], int left, int right)
{
if (left < right)
{
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
merge_sort(a, result, left, mid);
merge_sort(a, result, mid + 1, right);
merge(a, result, left, mid, right);
}
}
Procedure 𝐇𝐞𝐚𝐩-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
- Keep a copy of the root item
- Remove last item and put it to root
- Maintain heap property
- Return the copy of the root item
One possible implementation with C++:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// maintain heap property
void heapify(int arr[], int n, int i)
{
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
int largest = i;
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest])
largest = left;
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest])
largest = right;
if (largest != i)
{
swap(arr[i], arr[largest]);
heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
void heapSort(int arr[], int n)
{
// build max heap
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, n, i);
// swap the root item with the last item,
// then heapify the remaining items
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
Procedure 𝐒𝐞𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
Basic idea: pick out minimum element from input, then recursively sort remaining elements, and finally concatenate the minimum element with sorted remaining elements.
In: An array $A$ of $n$ integers.
Out: A permutation of that array $A$ that is sorted (monotonic).
SelectionSort($A$):
for $i := 1$ to $A.length$
$minIdx := i$
for $j := i + 1$ to $A.length$
if $A[j] < A[minIdx]$
$minIdx := j$
$Swap(i, minIdx)$
One possible implementation with C++:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
void SelectSort(int* arr, int n)
{
// 保存参与单趟排序的第一个数和最后一个数的下标
int begin = 0, end = n - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
int maxIndex = begin; // 保存最大值的下标
int minIndex = begin; // 保存最小值的下标
// 找出最大值和最小值对应的下标
for (int i = begin; i <= end; ++i)
{
if (arr[i] < arr[minIndex])
minIndex = i;
if (arr[i] > arr[maxIndex])
maxIndex = i;
}
// 最小值放在序列开头
swap(&arr[minIndex], &arr[begin]);
// 如果最大值原本在 begin 位置,即 maxIndex == begin,
// 那么上面的操作会将最大值换到下标为 minIndex 处,
// 此时 maxIndex 不再是最大值的下标,而是最小值的。
// 为了防止以上情况发生,我们需要更新一下 maxIndex。
if (begin == maxIndex)
maxIndex = minIndex;
// 最大值放在序列结尾
swap(&arr[maxIndex], &arr[end]);
++begin;
--end;
}
}
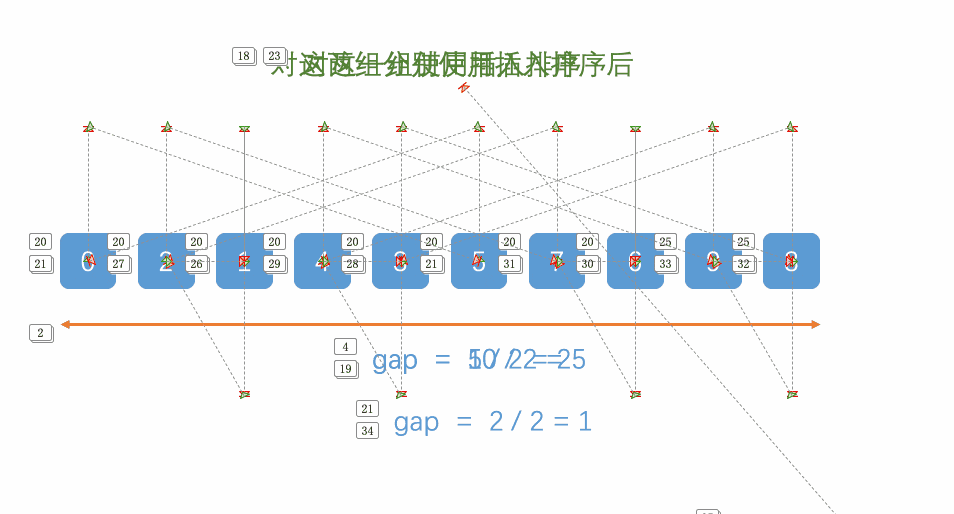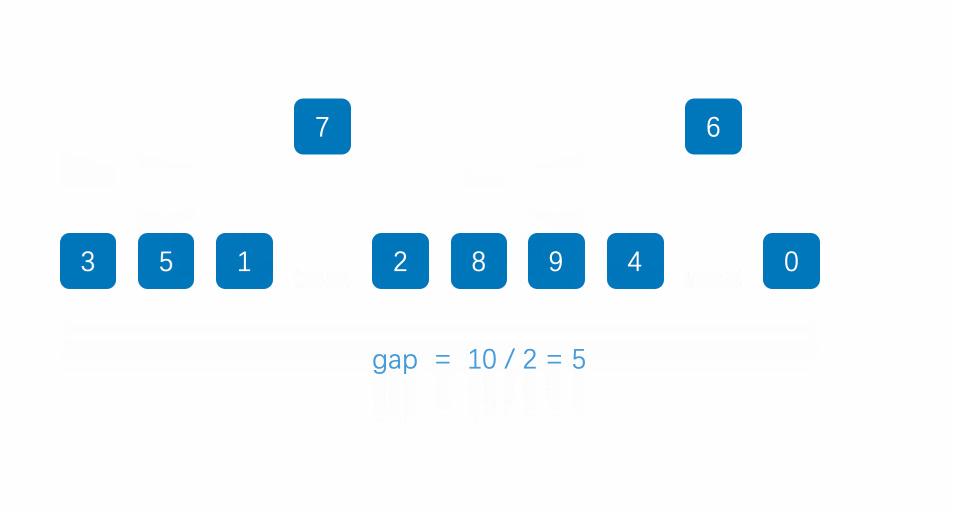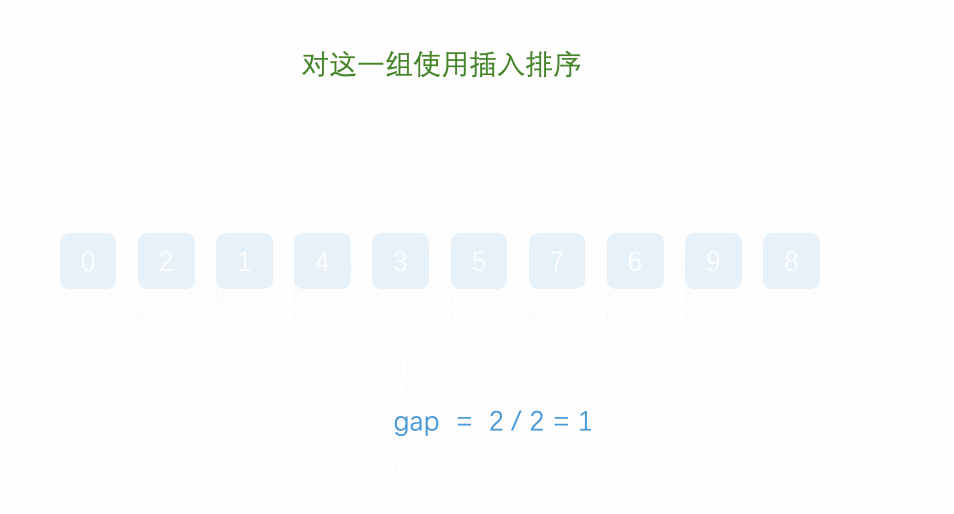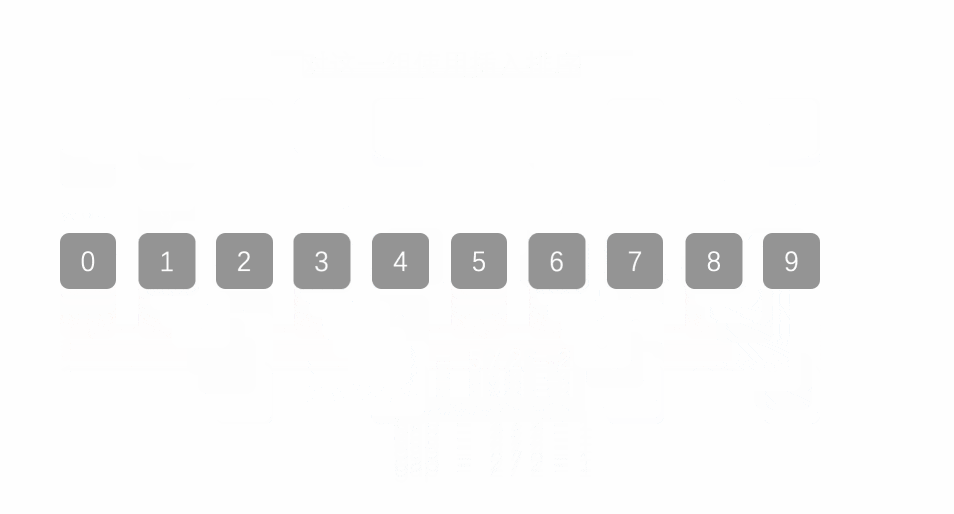
Procedure 𝐒𝐡𝐞𝐥𝐥-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
One possible implementation with C++:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void ShellSort(vector<int> &nums)
{
int size = nums.size();
for (int gap = size / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2)
{
// 使用插入排序对当前间隔进行排序
for (int i = gap; i < size; i++)
{
int key = nums[i];
int j = i;
while (j >= gap && nums[j - gap] > key)
{
nums[j] = nums[j - gap];
j -= gap;
}
nums[j] = key;
}
}
}
Procedure 𝐁𝐮𝐛𝐛𝐥𝐞-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
Basic idea: repeatedly step through the array, compare adjacent pairs and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. Thus, larger elements “bubble” to the “top”.
In: An array $A$ of $n$ integers.
Out: A permutation of that array $A$ that is sorted (monotonic).
BubbleSort($A$):
for $i := A.length$ down to $2$
for $j := 1$ to $i - 1$
if $A[j] > A[j + 1]$
$Swap(A[j], A[j + 1])$
One possible implementation with C++:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
void BubbleSort(int arr[], int len)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
Procedure 𝐐𝐮𝐢𝐜𝐤-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
Basic idea: Given an array $A$ of $n$ items.
- Choose one item $x$ in $A$ as the pivot.
- Use the pivot to partition the input into $B$ and $C$, so that items in $B$ are $\leq x$, and items in $C$ are $> x$.
- Recursively sort $B$ and $C$.
- Output $⟨B, x, C⟩$.
In: An array $A$ of $n$ integers.
Out: A permutation of that array $A$ that is sorted (monotonic).
QuickSortAbs($A$):
$x := GetPivot(A)$
$<B, C> := Partition(A, x)$
$QuickSortAbs(B)$
$QuickSortAbs(C)$
return $Concatenate(B, x, C)$
One possible implementation with C++:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// 选定一个 pivot 并将 left 到 right 之间的元素通过 pivot 划分成两部分,
// 使得 pivot 左边的元素都小于它,右边的元素都大于它,然后返回 pivot 的下标
int _partition(vector<int> &nums, int left, int right)
{
int pivot = nums[left]; // 令 pivot 为左边第一个元素
while (left < right)
{
// 如果右边元素大于 pivot,不管;反之,则让它到左边去
while (left < right && nums[right] >= pivot)
right--;
nums[left] = nums[right];
// 如果左边元素小于 pivot,不管;反之,则让它到右边去
while (left < right && nums[left] <= pivot)
left++;
nums[right] = nums[left];
}
nums[left] = pivot; // 最后记得恢复 pivot!!!
return left;
}
// 将 nums 通过 _partition 划分成两部分,对每个部分调用 _quick_sort
void _quick_sort(vector<int> &nums, int left, int right)
{
if (left < right)
{
int p = _partition(nums, left, right);
_quick_sort(nums, left, p - 1);
_quick_sort(nums, p + 1, right);
}
}
void QuickSort(vector<int> &nums)
{
_quick_sort(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
Procedure 𝐁𝐮𝐜𝐤𝐞𝐭-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
- Create $d$ empty lists. (These are the buckets.)
- Scan through input, for each item, append it to the end of the corresponding list.
- Concatenate all lists.
This algorithm only takes $\Theta(n)$ time.
- This is not a comparison based algorithm.
- No comparison between items are made.
- Instead the algorithm uses actual values of the items.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
void bucketSort(vector<int> &nums)
{
int n = nums.size();
int mn = nums[0], mx = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
mn = min(mn, nums[i]);
mx = max(mx, nums[i]);
}
int size = (mx - mn) / n + 1; // size 至少要为1
int cnt = (mx - mn) / size + 1; // 桶的个数至少要为1
vector<vector<int>> buckets(cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int idx = (nums[i] - mn) / size;
buckets[idx].push_back(nums[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
sort(buckets[i].begin(), buckets[i].end());
}
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].size(); j++)
{
nums[index++] = buckets[i][j];
}
}
}
Procedure 𝐑𝐚𝐝𝐢𝐱-𝐒𝐨𝐫𝐭
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
int maxbit(int data[], int n) // 辅助函数,求数据的最大位数
{
int maxData = data[0]; // 最大数
// 先求出最大数,再求其位数,这样有原先依次每个数判断其位数,稍微优化点。
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
if (maxData < data[i])
maxData = data[i];
}
int d = 1;
int p = 10;
while (maxData >= p)
{
maxData /= 10;
++d;
}
return d;
}
void radixsort(int data[], int n) // 基数排序
{
int d = maxbit(data, n);
int *tmp = new int[n];
int *count = new int[10]; // 计数器
int i, j, k;
int radix = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= d; i++) // 进行 d 次排序
{
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++)
count[j] = 0; // 每次分配前清空计数器
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
k = (data[j] / radix) % 10; // 统计每个桶中的记录数
count[k]++;
}
for (j = 1; j < 10; j++)
count[j] = count[j - 1] + count[j]; // 将 tmp 中的位置依次分配给每个桶
for (j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) // 将所有桶中记录依次收集到 tmp 中
{
k = (data[j] / radix) % 10;
tmp[count[k] - 1] = data[j];
count[k]--;
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) // 将临时数组的内容复制到 data 中
data[j] = tmp[j];
radix = radix * 10;
}
delete[] tmp;
delete[] count;
}
Summary
| Algorithms | Best | Worst | Average | In/Out-Place | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion-Sort | $O(n^2)$ | $O(n^2)$ | $O(n^2)$ | In-place | True |
| Merge-Sort | $O(n\log{n})$ | $O(n\log{n})$ | $O(n\log{n})$ | Out-place | True |
| Heap-Sort | $O(n\log{n})$ | $O(n\log{n})$ | $O(n\log{n})$ | In-place | False |
| Selection-Sort | $O(n^2)$ | $O(n^2)$ | $O(n^2)$ | In-place | False |
| Shell-Sort | $O(n\log{n})$ | $O(n^2)$ | - | In-place | False |
| Bubble-Sort | $O(n)$ | $O(n^2)$ | $O(n^2)$ | In-place | True |
| Quick-Sort | $O(n\log{n})$ | $O(n\log{n})$ | $O(n\log{n})$ | In-place | False |
| Bucket-Sort | $O(n + k)$ | $O(n^2)$ | $O(n + k)$ | Out-place | True |
| Radix-Sort | $O(n \cdot k)$ | $O(n \cdot k)$ | $O(n \cdot k)$ | Out-place | True |