🧑🏻💻 图的遍历
在 C++ 中,实现图的遍历的两种方式,即广度优先搜索(BFS)和深度优先搜索(DFS)。作笔记用。
🧑🏻💻 图的遍历
广度优先搜索
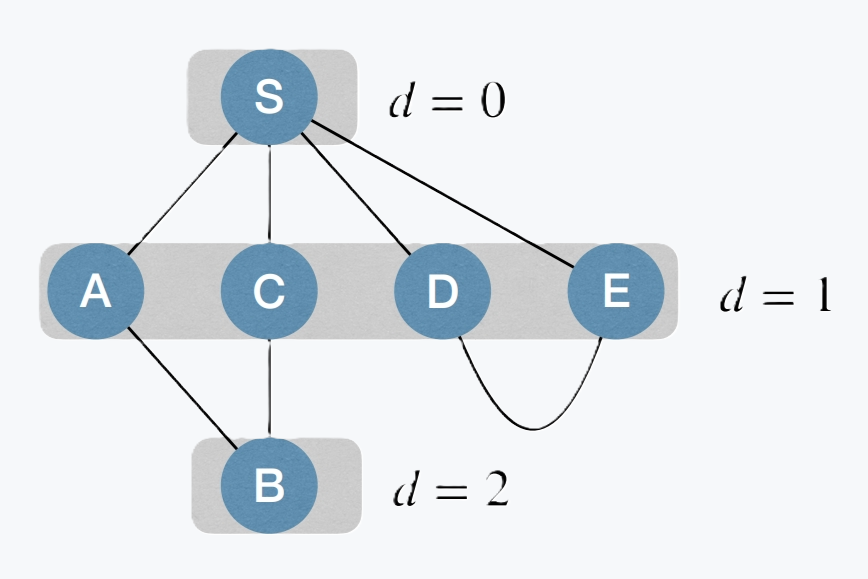
- Basic Idea of BFS:
- Start at the source node $s$;
- Visit other nodes (reachable from $s$) “layer by layer”
- How to implement BFS?
- Use a FIFO Queue!
- Nodes have 3 status:
- Undiscovered: Not in queue yet.
- Discovered but not visited: In queue but not processed.
- Visited: Ejected from queue and processed.
- What if the graph is not connected?
- Easy, do a BFS for each connected component!
BFSSkeleton(G, s):
for each $u$ in $V$
$u.dist := INF, u.discovered := False,$
$s.dist := 0, s.discovered := True$
$Q.enque(s)$
while $!Q.empty()$
$u := Q.dequeue()$
for each $edge(u, v)$ in $E$
if $!v.discovered$
$v.dist := u.dist + 1$
$v.discovered := True$
$Q.enque(v)$
示例代码:打印一号点到其余每一个点的最短路程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
// Author: Chen Xin
// Date: 2024-11-25
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
private:
int n;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
public:
Graph(int verticles);
void addEdge(int u, int v);
void findShortest();
};
Graph::Graph(int verticles)
{
n = verticles;
graph.resize(verticles);
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
void Graph::findShortest()
{
queue<int> discovered;
vector<int> distToFirst(n, -1);
discovered.push(0);
distToFirst[0] = 0;
// BFS
while (!discovered.empty())
{
int prev = discovered.front();
discovered.pop();
for (int neighbor : graph[prev])
{
if (distToFirst[neighbor] == -1)
{
distToFirst[neighbor] = distToFirst[prev] + 1;
discovered.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (i < n)
cout << distToFirst[i] << " ";
else
cout << distToFirst[i] << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int N, M, u, v;
cin >> N >> M;
Graph graph(N);
while (M--)
{
cin >> u >> v;
graph.addEdge(u - 1, v - 1);
// 题中顶点编号为 1 ~ N,实际存储时为 0 ~ (N-1),故进行转换
}
graph.findShortest();
return 0;
}
深度优先搜索
- Basic Idea of DFS, much like exploring a maze:
- Use a ball of string and a piece of chalk.
- Follow path (unwind string and mark at intersections), until stuck (reach dead-end or already-visited place).
- Backtrack (rewind string), until find unexplored neighbor (intersection with unexplored direction).
- Repeat above two steps.
- What if the graph is not (strongly) connected?
- Do DFS from multiple sources.
DFSSkeleton(G, s):
$s.visited := True$
for each $edge(s, v)$ in $E$
if $!v.visited$
$DFSSkelecton(G, v)$
DFSIterSkeleton(G, s):
Stack $Q$
$Q.push(s)$
while $!Q.empty()$
$u := Q.pop()$
if $!u.visited$
$u.visited := True$
for each $edge(u, v)$ in $E$
$Q.push(v)$
示例代码:判断图中是否存在环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
// Author: Chen Xin
// Date: 2024-11-25
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define UNVISITED -1
#define VISITING 0
#define VISITED 1
class Graph
{
private:
vector<vector<int>> graph;
int n;
public:
Graph(int verticles);
void addEdge(int u, int v);
bool findCycle();
bool DFS(int index, vector<int> &isVisited);
};
Graph::Graph(int verticles)
{
n = verticles;
graph.resize(verticles);
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
graph[u].push_back(v);
}
bool Graph::findCycle()
{
vector<int> isVisited(n, UNVISITED);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (isVisited[i] == UNVISITED)
{
if (DFS(i, isVisited))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Graph::DFS(int index, vector<int> &isVisited)
{
isVisited[index] = VISITING;
for (int node : graph[index])
{
if (isVisited[node] == UNVISITED)
{
if (DFS(node, isVisited))
return true;
}
// 节点正在被访问,说明存在环
else if (isVisited[node] == VISITING)
return true;
}
isVisited[index] = VISITED;
return false;
}
int main()
{
int N, M, u, v;
cin >> N >> M;
Graph graph(N);
while (M--)
{
cin >> u >> v;
graph.addEdge(u - 1, v - 1);
// 题中顶点编号为 1 ~ N,实际存储时为 0 ~ (N-1),故进行转换
}
cout << (graph.findCycle() ? "YES" : "NO") << endl;
return 0;
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权